
|
|
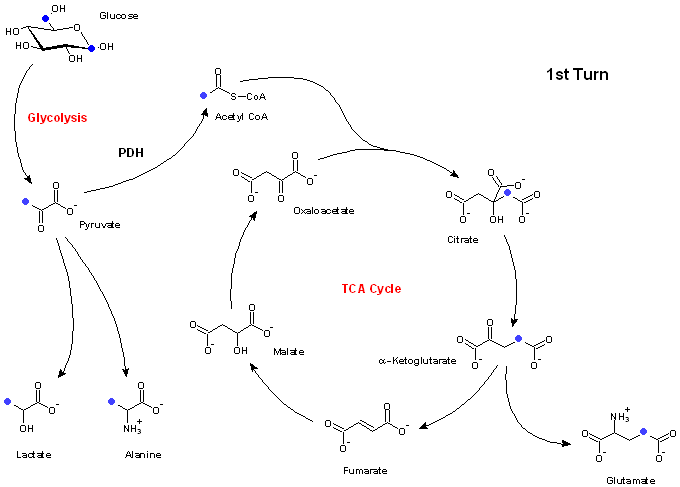
| During glycolysis [1,6-13C2]glucose – composed of six carbons – is cleaved in two three-carbon fragments leading to the formation of two pyruvate molecules which are labeled at the C3 position. Afterwards the label can pass into lactate and alanine, respectively, or it enters via acetyl coenzyme A (CoA) the TCA cycle. Subsequently, the 13C label may either directly quit the cycle incorporated at the C4 position of glutamate or ... | |